Secure and reliable Wireless Networking
The IoT Revolution for commercial Buildings
Fortsetzung des Artikels von Teil 1
PRE-Compliance with European Standards
The VdS label is a seal of quality and is the most important quality indicator for those responsible for safety security systems when deciding, purchasing, integrating and installing security technology and security services — especially in commercial buildings. Organized in association with other European countries, the Association of Property Insurers is also recognized worldwide in its sphere of activity. A VdS certificate allows security-relevant systems to be approved after they have been checked for security, reliability and more. The aim is to use the tested techniques to reduce the risk of damage and ultimately to prevent damage prematurely.
The technical hurdles are enormous in order to obtain a VdS certified product and system. If a manufacturer is interested in having a product certified with a wireless link, this manufacturer must make large investments in order to ultimately develop its proprietary wireless technology for safety-critical applications. As it is important that there is no interference with safety-related applications, this wireless technology still has to pass lengthy.
In years of cooperation with the VdS, the IP500 Alliance has successfully developed a robust and reliable wireless IoT standard in a first step of pre-conformity — according to EN 50131-5-3 [2] — for some important applications required to establish IoT platform. This pre-conformity allows the members of the IP500 Alliance tocertify their products, which are equipped with an IP500 wireless module (CNX200), without additional development effort and other pre-conformity testing for the VdS. This results in considerable time and cost savings for the manufacturer.
Wireless-Technology for the highest Demands
In order to meet all requirements to achieve conformity and interoperability, the members and partners of the IP500 Alliance have coordinated and developed the entire IP500 system at all three levels (layers). The three levels are:
- Wireless transmission (PHY / MAC).
- Network stack and application.
- Protocol, infrastructure, gateway and database.
The first two levels — wireless transmission and network stack — are closely coordinated and essentially form a unit, as the example of true dual-band technology with mesh topology shows. In this case, the PHY level provides both frequencies simultaneously and the network stack level automatically routes the data packets depending on the interference in one of the bands to the target node, a gateway or a terminal device.
Advantages of the IP500 Standard on the Wreless Level
Due to the requirements from the system level, OQPSK (Offset Quadrature Phase-Shift Keying) was chosen for modulation. The basis for this is the IEEE standard 802.15.4 (2006), which provides OQSPK for higher data rates in the 2.4 GHz band. Due to the system requirements of the security applications, the simultaneous use of both bands — Sub-GHz and 2.4 GHz — was specified in the IP500 standard. This created a very high level of robustness against interference.
Combined with the asynchronous meshing process of the network stack, the IP500-PHY and network stack can avoid different interferences – both in the case of interference on the frequency level and in the event of interference on the routing path.
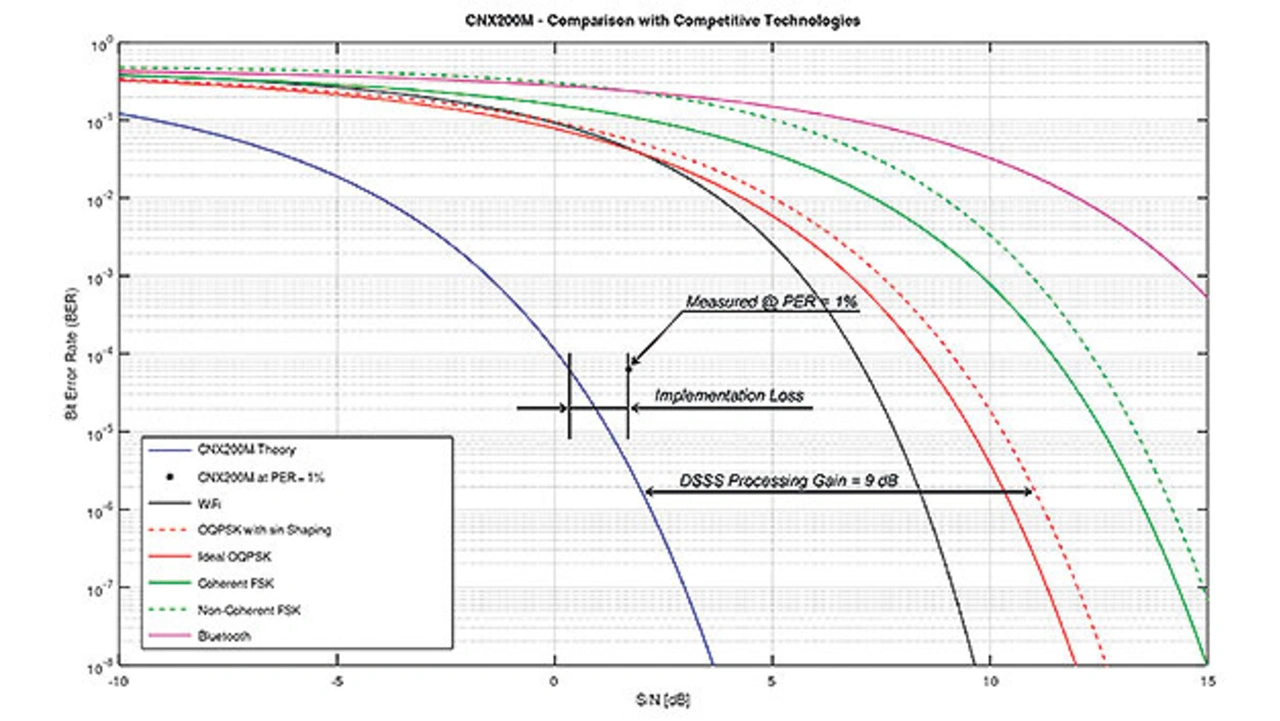
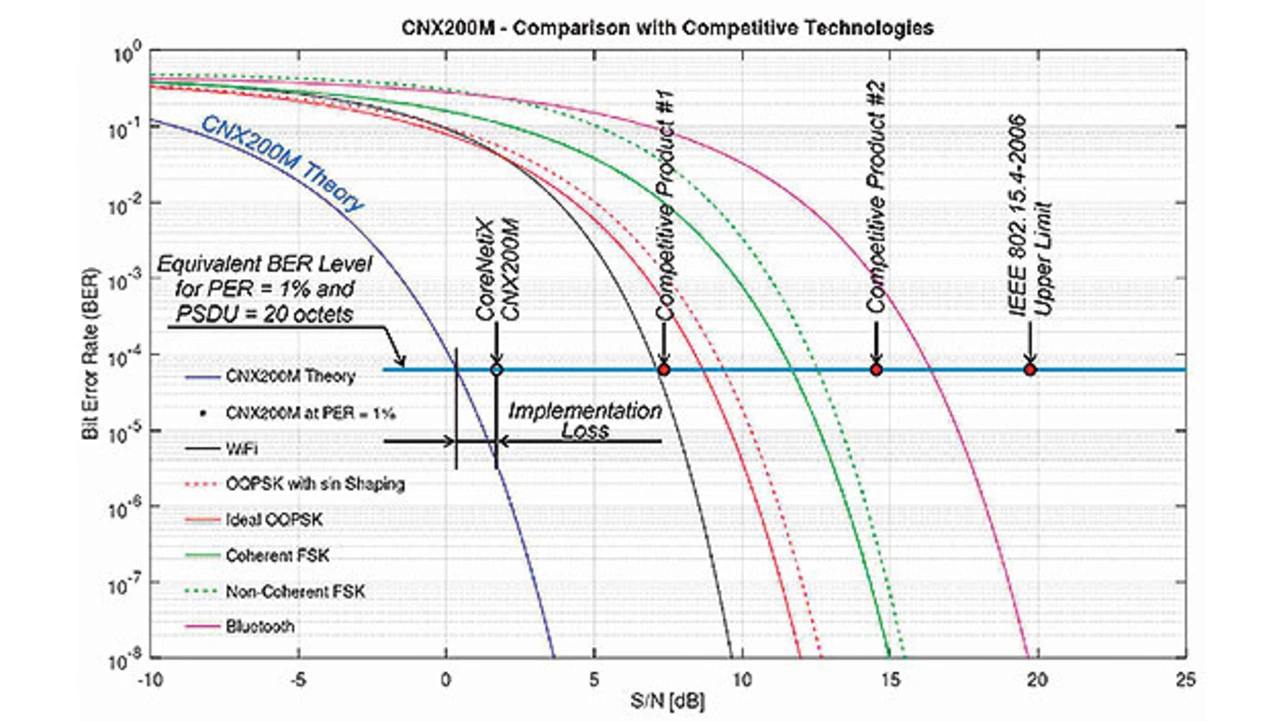
The measurement results in Figures 3 and 4, measured in a real environment with high interference, as are typical for buildings, tunnels or metallic environments (aircraft and ships), pro- vide an insight into the robustness of the IP500 standard compared to other wireless standards that are used worldwide.
It is advantageous to have a smaller signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) (position of the product further to the left in Figure 4) for several reasons:
- Higher link budget. Given the signal-to-noise ratio, the number of bits received incorrectly is reduced. For example: for SNR = 4 dB, the received messages from the IP500 wireless module CNX200M are error-free in practice. A bit error rate BER = 10-6 means one bad bit per million received bits. In comparison, for the same SNR = 4 dB, the BER for Wi-Fi = 0.01, that is one bad bit per 100 bits received. Under such conditions (SNR = 4 dB), wireless standards such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth or LoRa cannot be used practically.
- Reduce energy consumption — reliable transmission requires less RF transmission power with a small SNR. A closer look at the test results shows that the known wireless standards cannot be used extensively as a wireless IoT platform in a commercial or industrial environment, because lack of performance, robustness or security can significantly disrupt the IoT business processes.
The Network Level of the IP500 Standard
The construction of the IP500 network stack is responsible for the topology of the network, the scalability, the latency and the encryption of the data — and thus for the robustness and security in the entire IP500 network. Figure 5 shows the IP500 structure based on the well-known OSI model.
The asynchronous transmission method was selected in accordance with the IEEE 802.15.4 standard. html?aid=173266" href="https://www.elektroniknet.de/international/bilder/the-network-level-of-the-ip500-standard-figure-5-9-8624-Bild-2.html?aid=173266">Figure 6 shows the structure of a complete IP500 wireless data packet.
The Network Level of the IP500 Standard, Figure 5-9
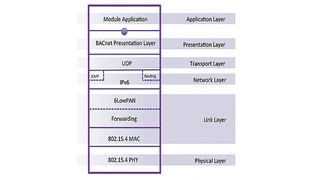
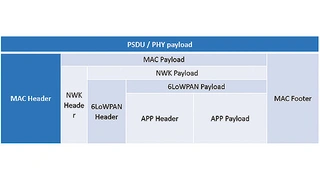
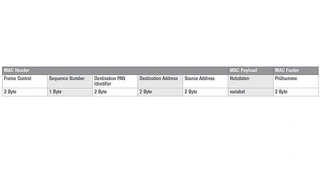
The main functions of the network are:
- Structure of the data packets (frames) and file headers (headers).
- Forwarding of the packets through the asynchronous mesh network using the routing table.
- Securing and encryption of data packets.
- The IoT Revolution for commercial Buildings
- PRE-Compliance with European Standards
- Routing by HOP List
- IP500 Alliance







