MOST Network and System
Building a MOST Infotainment System in a Networking Environement
Fortsetzung des Artikels von Teil 4
Convergence of automotive and consumer electronics
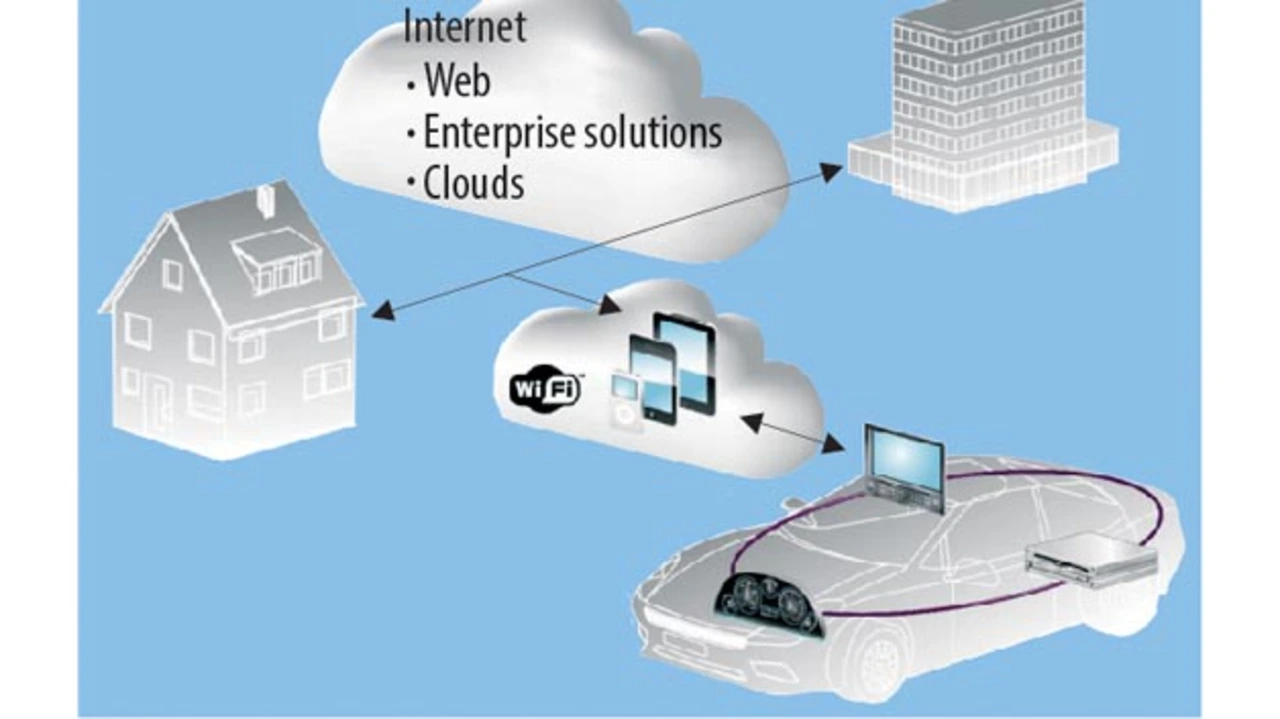
As mentioned before, future infotainment systems require a tool for support of the convergence between automotive and consumer electronics over computer networks. There are several variants of networking topologies regarding how consumer electronic devices such as mobile phones, tablets and laptops and the infotainment system could be connected. The simplest topology: the car has its own mobile broadband Internet connection and its own Wi-Fi hot spot. This provides access to the Internet and remote automotive services. Another topology is an analogy to the Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) concept. Here, the infotainment system has a Wi-Fi network interface and connects to the hot spot provided by the customer mobile device, which has Internet access over a cellular network.
The principal difference between these two topologies: In the first case, the infotainment system communicates with the service endpoints in the Internet directly, whereas in the second case the network address translation (NAT) takes place between the communication partners. Moreover, enterprise systems have even more complex topologies, including firewalls, virtual private networks (VPN), etc. In this situation a greater reach for applications is necessary.
It should be noted that some parts of the infotainment system, such as navigation components, can use Internet services e.g. to update the traffic information on a route. It means that service providers as well as consumers of these services may be deployed on automotive and mobile devices and also on the Internet. Software applications that offer a service or consume it, especially over a network, are called service-oriented applications.
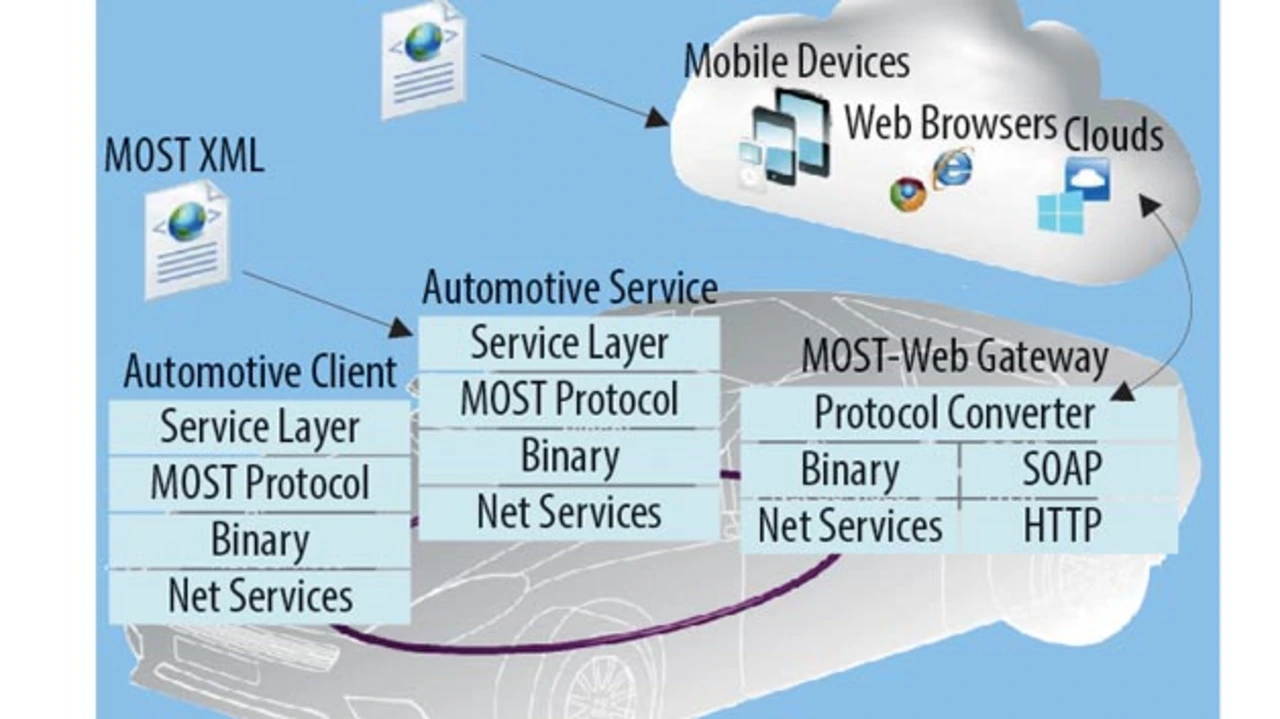
A part of the .NET framework for building service-oriented applications is the Windows Communication Foundation (WCF). The conceptual model that supports the service orientation is called Service Oriented Architecture (SOA). There is a wide range of technologies such as Web services (WS) or Representational State Transfer (REST) that can be used to implement SOA. The WCF supports the most common technologies.
In WCF, a .NET interface defined in the code or generated from a Web Services Description Language (WSDL) file specifies the contract of a service. The class that implements this interface to deploy on the server is called service class. The instance of this class can be hosted in a desktop application, a Web server or in Windows Azure, the Microsoft cloud platform. K2L ATS paves the way for connecting MOST and WCF to simulate the new features provided by the vehicle-Web interconnection.
With the MAG.NET tool, the user can select MOST functions from a function block to create the .NET interface as a service contract. The K2L ATS framework includes the .NET class, which implements the MOST WCF gateway. It receives an incoming message from the MOST function and transforms its data to the parameters of the corresponding method for the specified WCF interface. After this, the gateway-class calls the method of the instance of the service class that implements this WCF interface. This instance can be a client proxy that accesses the service hosted outside the MOST network. It can also be a service implementation available in MOST, as well as on the Internet or in a local area network, for example, over HTTP.
The client or service can be implemented on other platforms. The tool svcutil.exe (part of Windows SDK) can be used to generate the WSDL file from the .NET interface. The WSDL file serves as an input for other tool chains to implement services or to generate client code for other programming languages or platforms such as C++ or JavaScript.
This approach shows that MOST, as the dedicated technology for infotainment networking, already contains the elements that are suited for communication with the services deployed on the Internet. The solid methodology (top-down) used to build a MOST based infotainment system is close to the development process of enterprise Web services. An integration of the best parts of these technologies opens up new and interesting opportunities for MOST applications.
- Building a MOST Infotainment System in a Networking Environement
- Software development process
- Simulation of device behaviour
- In the focus: the Automotive Test Solution
- Convergence of automotive and consumer electronics
- The author: